Content Marked with: Robert Allen

Cleaner East Asian air unmasks a much hotter planet
One of the most pressing mysteries in climate science is why Earth has begun warming faster over the past 15 years. A new international study points to a surprising contributor: cleaner air in East Asia, particularly China. The study, published in Communications Earth & Environment, found that East Asia’s aerosol reductions contributed about 0.05 degrees...
By Jules Bernstein |

Does planting trees really help cool the planet?
Replanting forests can help cool the planet even more than some scientists once believed, especially in the tropics. But even if every tree lost since the mid-19 th century is replanted, the total effect won’t cancel out human-generated warming. Cutting emissions remains essential. In a new modeling study published in Communications Earth & Environment, researchers...
By Jules Bernstein |

Improving air quality increases forest fires
If we want cleaner air, fewer forest fires, and less severe climate change, a new UC Riverside study shows we must reduce aerosol pollution and greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide at the same time. The study found that boreal forests in the northern hemisphere are particularly vulnerable to negative effects of cleaning up aerosol pollution...
By Jules Bernstein |

CO2 worsens wildfires by helping plants grow
By fueling the growth of plants that become kindling, carbon dioxide is driving an increase in the severity and frequency of wildfires, according to a UC Riverside study. The worldwide surge in wildfires over the past decade is often attributed to the hotter, drier conditions of climate change. However, the study found that the effect...
By Jules Bernstein |
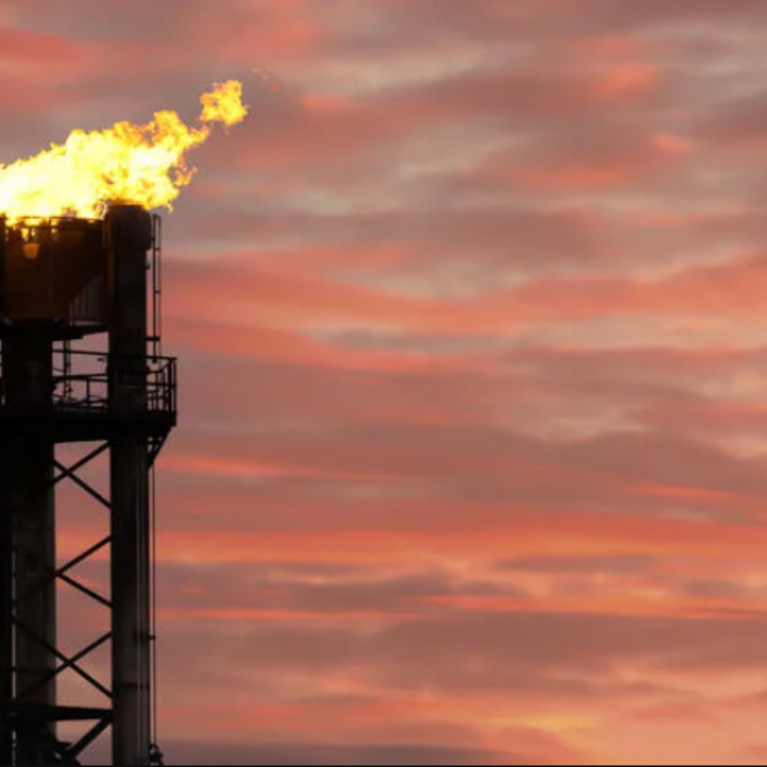

Surprise effect: Methane cools even as it heats
Most climate models do not yet account for a new UC Riverside discovery: methane traps a great deal of heat in Earth’s atmosphere, but also creates cooling clouds that offset 30% of the heat. Read More
By JULES BERNSTEIN |
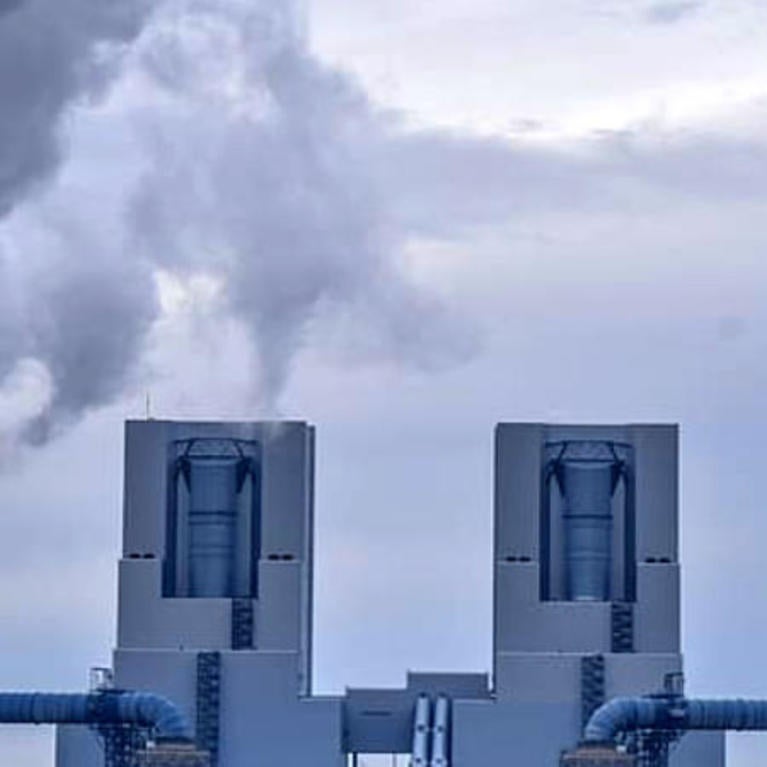

Reducing aerosol pollution without cutting carbon dioxide could make the planet hotter
Humans must reduce carbon dioxide and aerosol pollution simultaneously to avoid weakening the ocean’s ability to keep the planet cool, new research shows. Aerosol pollution refers to particles in the air emitted by vehicles and factories that burn fossil fuels. This pollution contributes to asthma, bronchitis, and long-term irritation of the respiratory tract, which can...
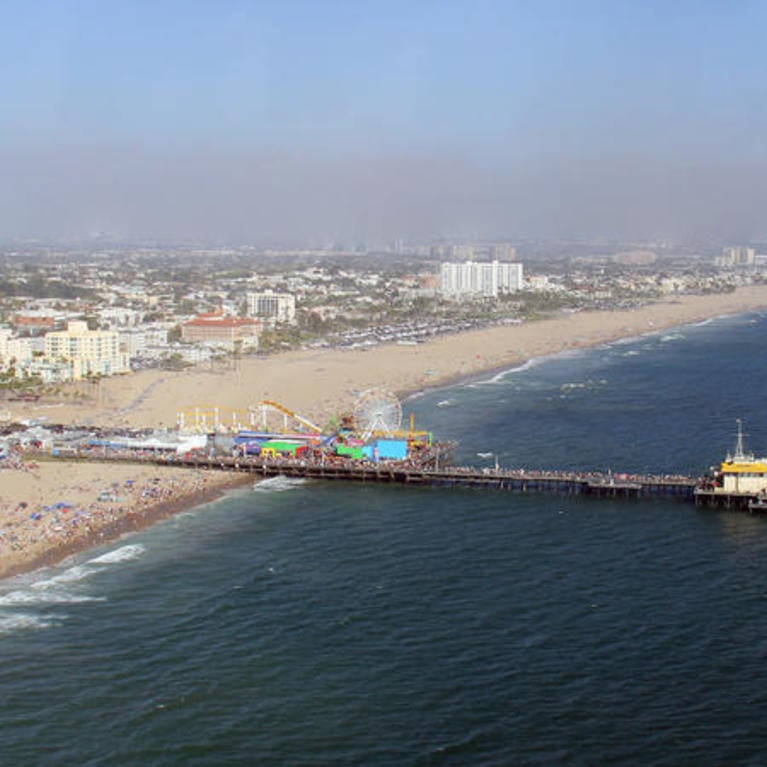

A warming world increases air pollution
Climate change is warming the ocean, but it’s warming land faster and that’s really bad news for air quality all over the world, says a new University of California, Riverside study. The study, published February 4 in Nature Climate Change, shows that the contrast in warming between the continents and sea, called the land-sea warming...
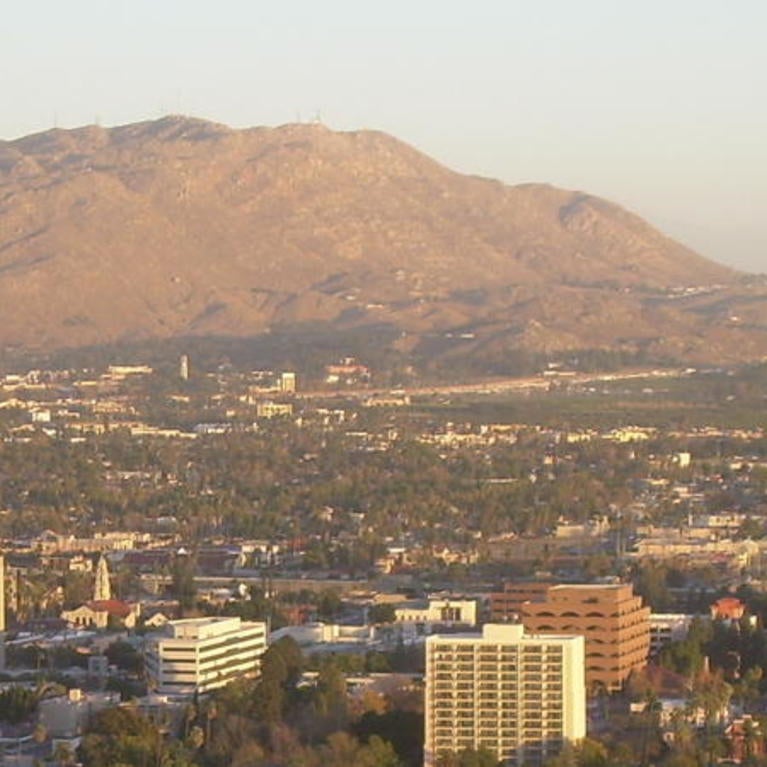

Global Warming, El Niño Could Cause Wetter Winters, Drier Conditions in Other Months
"RIVERSIDE, Calif. ( www.ucr.edu) — So here’s the good news: Despite fears to the contrary, California isn’t facing a year-round drought in our warming new world. However, UC Riverside Earth Sciences Professor Robert Allen’s research indicates that what precipitation the state does get will be pretty much limited to the winter months — think deluge-type...
California Projected to Get Wetter Through This Century
"Under business-as-usual greenhouse gas emissions, climate models predict California will get warmer during the rest of the century and most also predict the state will get drier." Read More
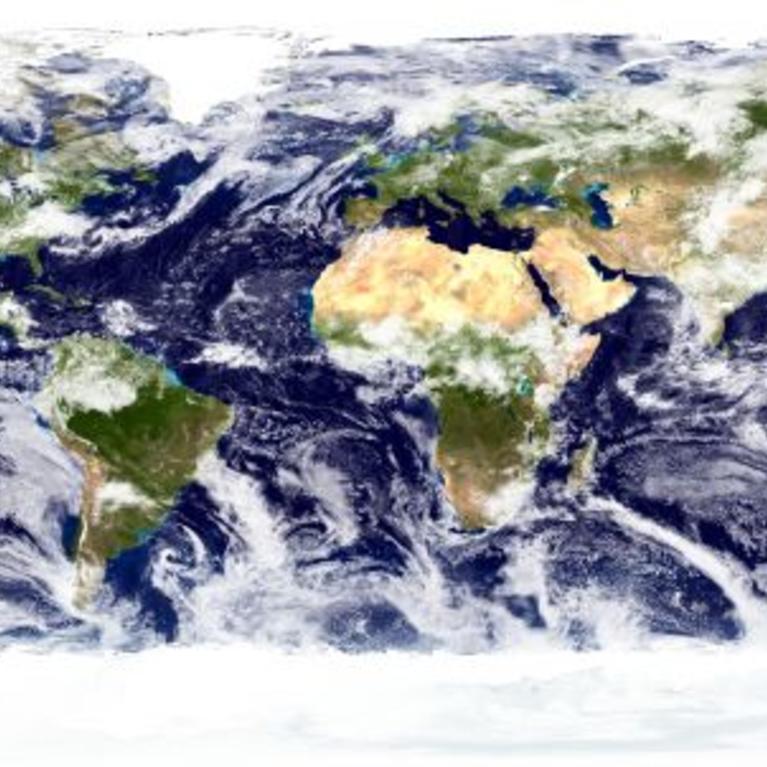
Clouds are Moving Higher, Subtropical Dry Zones Expanding
"A University of California, Riverside assistant professor and a team of researchers have found that the cloudy storm tracks on Earth are moving toward the poles and subtropical dry zones are expanding. Cloud tops are also moving higher in the atmosphere. The findings, based on satellite cloud records, confirm computer climate models that have predicted...
Let us help you with your search